

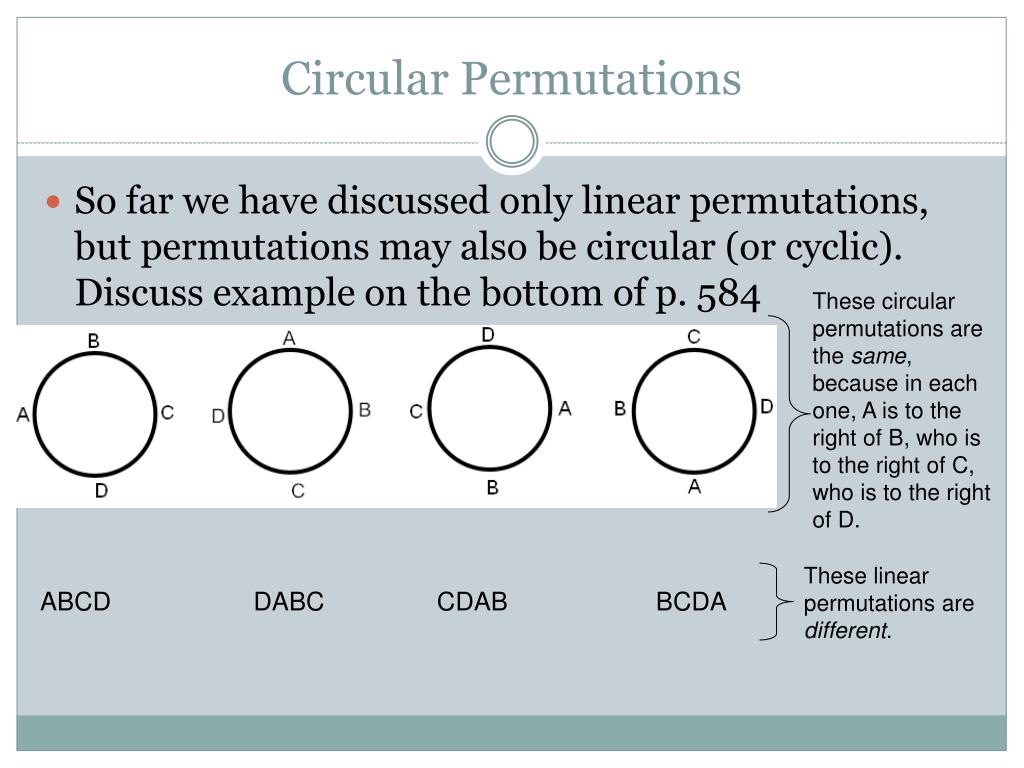
When connected together by a series of peptide bonds, amino acids form a polypeptide, another word for protein. The defining feature of an amino acid is its side chain (at top, blue circle below, all colored circles). What are the circles in a protein molecule? What is circular permutation?Ĭircular permutation is the total number of ways in which n distinct objects can be arranged around a fix circle. From: Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science, 2013. Green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a fluorescent protein that was originally isolated from the luminous organ of the jellyfish Aequorea victoria by Dr.
Reporter gene fusions based on the enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) are powerful experimental tools that allow real-time changes in gene expression to be monitored both in single cells and in populations. This Emerald FP has improved photostability and brightness than EGFP. Protein engineering of EGFP has yielded several green variants with improved characteristics such as Emerald. Read More: What is the River that flows in Algeria? Why is EGFP better than GFP?ĮGFP is brighter and matures rapidly at 37☌ than wild-type GFP. Photoactivatable fluorescent proteins (PA-FPs) are fluorescent proteins that display unique changes in their spectral properties upon exposure to a specific wavelength of light. How does Photoactivatable fluorescent protein work? … Thus, PA–GFP is an excellent tool for monitoring the dynamic subcellular localization of fusion proteins. In particular, the photoactivatable GFP (PA–GFP) has been utilized for monitoring protein movement within living mammalian cells (Lippincott-Schwartz and Patterson, 2008 Patterson and Lippincott-Schwartz, 2004). How do you solve for circular permutation? What does Photoactivatable mean?įilters. The T4 genome is circularly permuted and terminally redundant with respect to base sequence these features protect against information loss during replication of a linear DNA. Why the T4 phage genome is circularly permuted?īacteriophage T4 contains a large, linear double-stranded DNA genome, with chemical modifications of its cytosine residues. The result is a protein structure with different connectivity, but overall similar three-dimensional (3D) shape. What is circular permutation genetics?Ī circular permutation is a relationship between proteins whereby the proteins have a changed order of amino acids in their peptide sequence. The key difference between GFP and EGFP is that the GFP is a wild-type protein incorporated in the molecular cloning of non-mammalian cells while the EGFP is an improved or engineered type of GFP that can be used on mammalian cells. What is the difference between EGFP and GFP? Photoactivatable fluorescent proteins (PAFPs) is a type of fluorescent protein that exhibit fluorescence that can be modified by a light-induced chemical reaction. Such a structure imparts greater mobility to the FP than that of the native variant, allowing greater lability of the spectral characteristics. In circularly permuted FPs (cpFPs), the original N- and C-termini are fused using a peptide linker, while new termini are formed near the chromophore.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
